Scope
This guideline covers antifungal treatment for cutaneous and oral Candida infection.
For genital thrush (male and female) please refer to Candida, genital thrush in the genital guidelines.
For nipple thrush please refer to nipple and breast thrush in pregnancy and postpartum guidelines.
For angular cheilitis please refer to the angular cheilitis in dental guidelines.
Systemic Candida infection, Candida infection of the ear canal and oesophageal candidiasis are outside the scope of this guideline.
Oesophageal candidiasis can be associated with immunocompromise including HIV infection and requires further investigation and referral to an appropriate specialist.
Comments from the Expert Advisory Group
Diagnosis is generally made on clinical grounds.
In case of treatment failure, it may be necessary to send samples for fungal culture.
Review modifiable risk factors in case of recurrence and refractory disease.
|
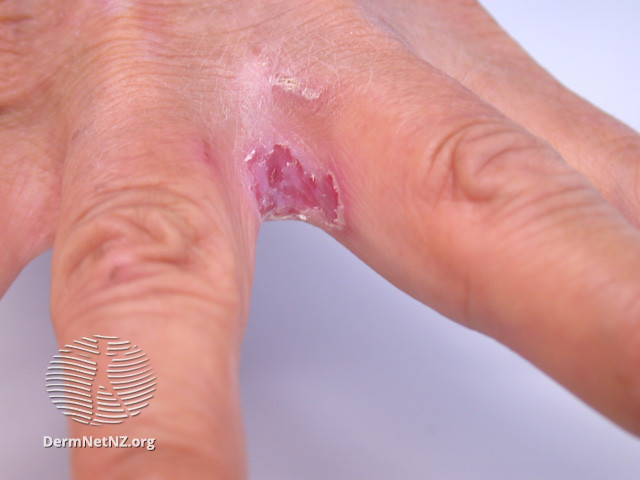 Image 1: cutaneous candidiasis Image 1: cutaneous candidiasis
 Image source/credit: Dermnet Image source/credit: Dermnet



|
 |
|
Image 2: cutaneous candidiasis
Image source/credit: Dermnet
|
 |
|
Image 3: infant oral candidiasis
Image source/credit: Dermnet
|
 |
|
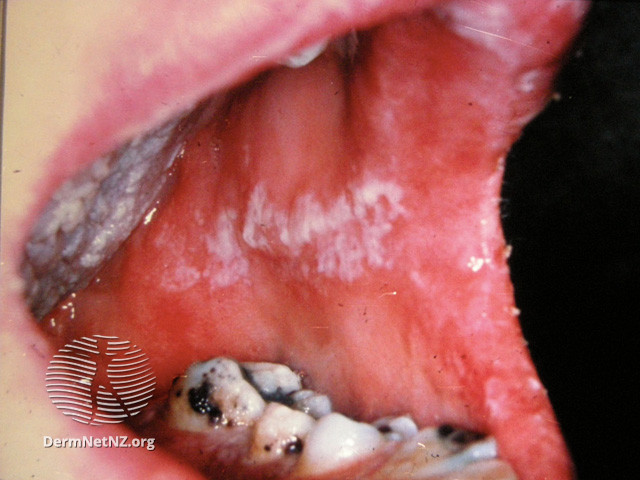
Image 4: adult oral candidiasis
Image source/credit: Dermnet


|
  |
Treatment
Cutaneous candidiasis
| Cutaneous candidiasis: 1st choice options (topical therapy) |
| Drug |
Dose |
Duration |
Notes |
| Clotrimazole 1% cream |
Apply every 8 to 12 hours |
4-6 weeks |
To prevent relapse, treatment should be continued for at least two weeks after the disappearance of all signs of infection |
|
OR
Miconazole 2% cream |
Apply to affected area every 12 hours
|
2-6 weeks |
Continue for 7 – 10 days after legions have healed
|
Oropharyngeal candidiasis
| Oropharyngeal candidiasis: 1st choice options |
| Drug |
Dose |
Duration |
Notes |
|
Miconazole 20mg/mL oral gel
|
Neonate: 1ml two to four times daily after feeds*
2-3 months: 1.25ml (quarter of measuring spoon provided) to be applied four times daily after feeds*
≥4 months: 1.25ml (quarter of measuring spoon provided) to be applied four times a day after feeds
Adults and children 2 years of age and older: 2.5ml (half of measuring spoon provided) to be applied four times a day after meals
|
The treatment should be continued for at least a week after the symptoms have disappeared
|
*Unlicensed use in infants < 4 months due to choking risk. Lower age limit increased to 5-6 months for infants who are pre-term or exhibiting slow neuromuscular development.
The gel should not be swallowed immediately, but kept in the mouth as long as possible.
The dose should be divided into smaller pea-sized portions; gel should be smeared in baby’s mouth after feeds with a clean finger, ensuring there are no clumps of gel in the mouth.
For oral candidiasis, dental prostheses should be removed at night and brushed with the gel.
Check for interactions before prescribing.
|
|
OR
|
|
Nystatin 100,000 units/ml oral suspension
|
Neonate: birth – 1 month: 1mL every 8 hours after feeds
Infant: 1 month – 2 years:
1-2mL every 6 hours after feeds
Adult and children > 2years: 1-6mL every 6 hours after meals
|
Usually for 7 days - continue for 48 hours after clinical cure, if signs and symptoms persist beyond 14 days re-evaluate
|
Keep suspension in contact with oral mucosa for as long as possible before swallowing or spitting out.
Larger volumes of nystatin may be required to provide adequate coverage of more extensive infections.
|
Systemic treatment – Adults (reserved for recurrent cutaneous or oropharyngeal candidiasis)
|
Cutaneous candidiasis (Adults) : systemic therapy (reserved for recurrent cutaneous candidiasis) |
| Drug |
Dose |
Duration |
Notes |
|
Fluconazole**
|
150 mg once weekly
|
2 to 4 weeks
|
Recurrent cutaneous candidiasis (as distinct from genital candidiasis) should be referred. See guideline for recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis
Use with caution in patients with hepatic dysfunction.
Avoid fluconazole (and all oral azoles) in pregnancy.
See HPRA caution in women of childbearing potential**
|
|
OR
Fluconazole**
|
50 mg once daily
|
2 to 4 weeks
|
|
Oropharyngeal candidiasis (Adults): systemic treatment
(reserved for recurrent oropharyngeal candidiasis)
As recurrent oropharyngeal candidiasis may indicate an underlying condition patients should be referred
|
|
Fluconazole**
|
Loading dose: 300mg on Day 1
Subsequent dose: 150mg once daily
|
7 to 21 days (until oropharyngeal candidiasis is in remission)
|
Longer periods may be used in patients with severely compromised immune function.
Use with caution in patients with hepatic dysfunction.
Avoid fluconazole (and all oral azoles) in pregnancy.
See HPRA caution in women of childbearing potential**
|
|
OR
Itraconazole***
|
100mg every 24 hours
|
14 days
|
Take capsules immediately after a meal for maximum absorption.
Not recommended in patients with active or chronic liver disease.
Avoid itraconazole (and all oral azoles) in pregnancy*** |
**Women of childbearing potential, for whom fluconazole is prescribed, should be informed of the potential risks to the foetus:
- After single dose treatment, a washout period of one week is recommended before pregnancy.
- For longer courses of treatment appropriate contraception should be considered throughout the treatment period and for one week after the final dose.
*** Women of childbearing potential taking itraconazole should use contraceptive precautions. Effective contraception should be continued until the menstrual period following the end of itraconazole therapy.
|
General Advice for Self-Care
Self-management of cutaneous candidiasis
Candidiasis is particularly likely to affect flexures in warm weather especially in those living with obesity. Keeping these areas dry, particularly skin folds can help prevent recurrence.
Self-management of oral candidiasis
Practice good oral hygiene
- Brush teeth regularly
- Use warm saline water as a mouth wash
- Avoid use/overuse of antiseptic mouthwashes, as they alter the flora of the mouth
- Rinse mouth out with water after using a steroid inhaler
- Smoking is a risk factor for oral candidiasis and smoking cessation should be considered
Denture wearers:
- Clean dentures with an anti-candidal preparation, such as 1% sodium hypochlorite solution
- Remove dentures overnight
Patient Information
- Doses are oral and for adults unless otherwise stated
- Renal impairment dosing table
- Safety in Pregnancy and Lactation
- Drug interactions table. Extensive drug interactions for clarithromycin, fluoroquinolones, azole antifungals and rifampicin. Many antibiotics increase the risk of bleeding with anticoagulants.
- Visit the Health Products Regulatory Authority (HPRA) website for detailed drug information (summary of product characteristics and patient information leaflets). Dosing details, contraindications and drug interactions can also be found in the Irish Medicines Formulary (IMF) or other reference sources such as British National Formulary (BNF) / BNF for children (BNFC).
Reviewed December 2022, minor update December 2023 and March 2025
